IDES Data Preparation
The International Data Exchange Service (IDES) is a secure managed file transfer service that allows financial institutions and tax authorities to securely send information on financial accounts held by U.S. taxpayers in accordance with the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA). Files transmitted via IDES must be encrypted and packaged in accordance with published data preparation instructions. The data preparation process is an important step to ensure that information transmitted via IDES conforms to U.S security standards to safeguard sensitive information.
The IDES Data Preparation Java project repository demonstrates a sample working application built using Java inside of Eclipse. An application was also developed using .Net, see IDES Data Preparation .Net for more information.
The example explains how to use the code to develop an application that will create an IDES data packet and decrypt notifications. The project starts with a validated FATCA XML file. The application does not validate the XML or metadata schemas. The sample application will digitally sign, encrypt, compress, and archive the data packet into a compliant .ZIP format.
Please note that there are many open market tools that produce the same results; however, the IRS does not endorse any commercial products, including the frameworks used in the example.
Application Setup
The sample application was created using Eclipse 4.5.1 and JRE version 1.8.0_65.
This repository includes a .zip file that contains several files necessary to this sample application. While some files can be copied and pasted from this guide, some must be downloaded from the .zip file and placed as indicated by the guide.
Keystore - This folder contains a set of .jks files containing self-signed test public and private keys used by the application.
Certs - This folder contains a few certificates in .crt format that are used by the test Config files.
lib - This folder contains the log4j-1.2.16.jar file which provides the console logging for the application.
generated - This folder has a set of .java files related to the metadata used by the application.
src - This folder has the main set of .java files, including testmain.java which is used to start the application.
Sample.000000.00000.TA.124_Payload.xml - This is the FATCA XML that will be signed, encrypted, and packaged by the application. This is a test file for the application and is not intended to portray a specific business case.
Create a New Project
Open Eclipse, select New, select Java Project.
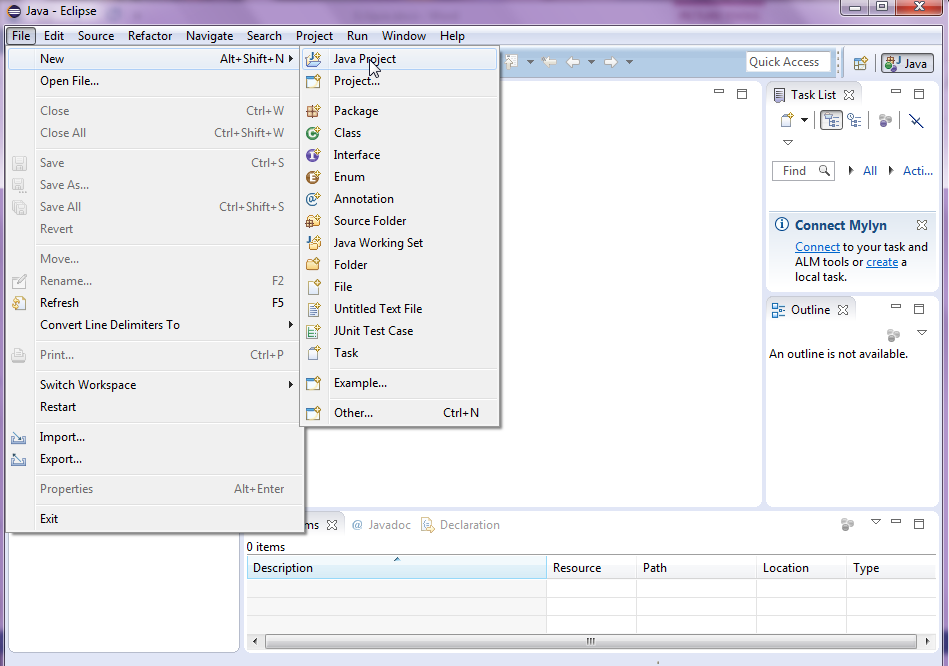
Figure 1
Enter IDESDataPreparation for the Project Name and select the JRE that you will use. The sample is using jre1.8.0_65. Click the Next button.
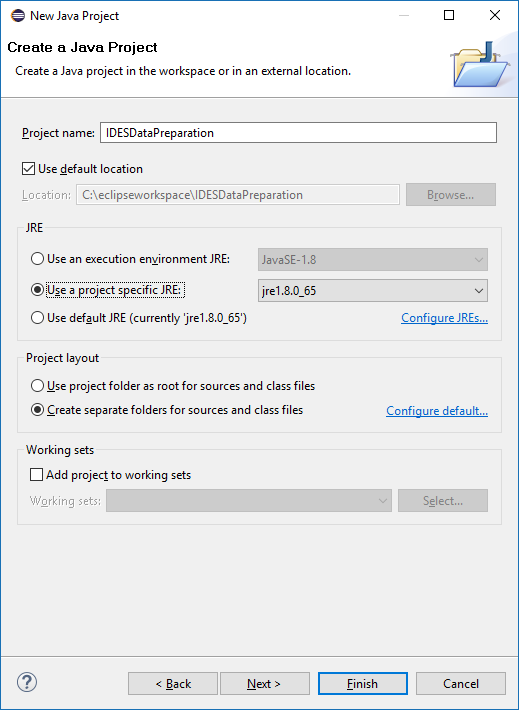
Figure 2
Click Finish, these will be set up later
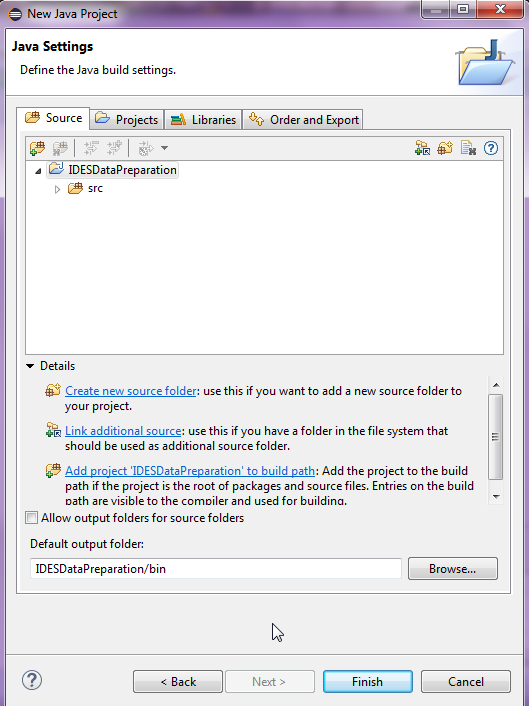
Figure 3
The Eclipse project with the default settings:
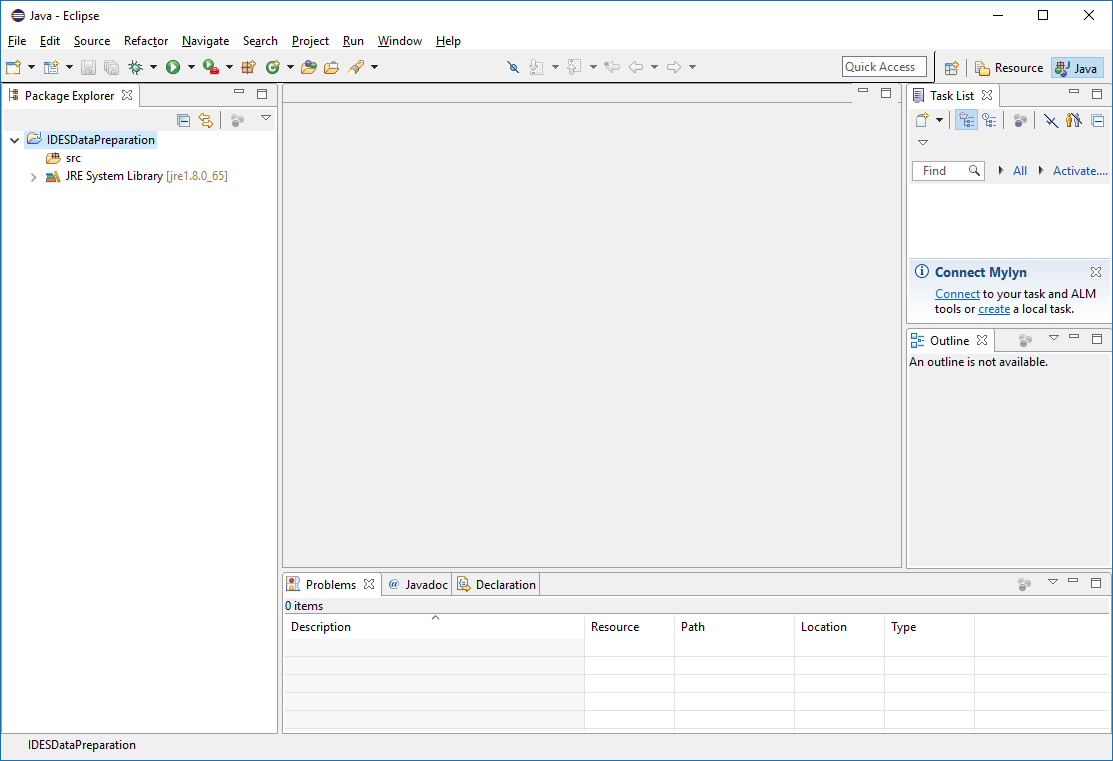
Figure 4
The file system for the new project:
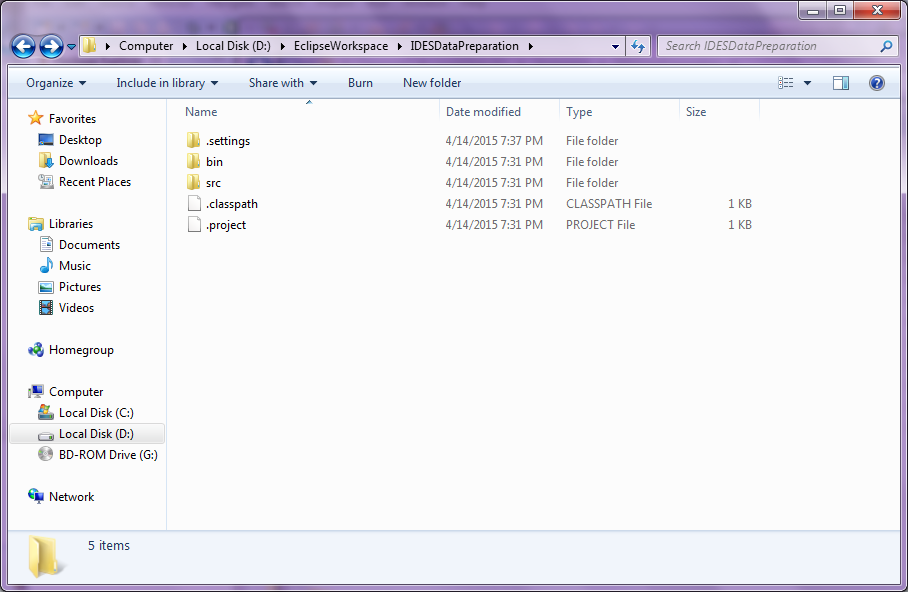
Figure 5
generated folder
Add the generated folder from the .zip repository into the IDESDataPreparation folder.
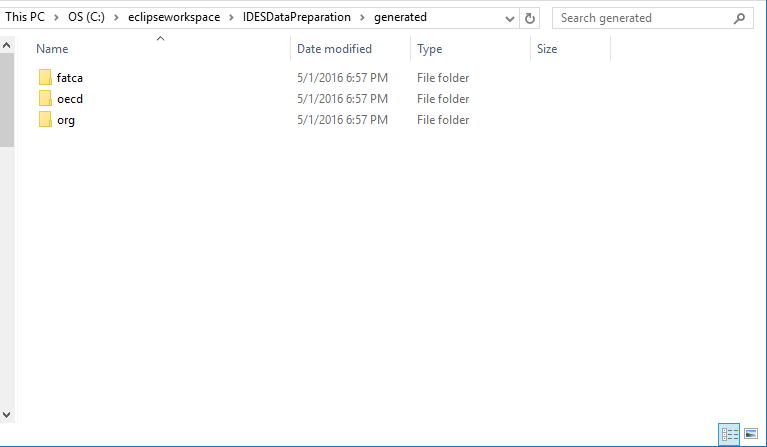
Figure 6
Keystore
Place the Keystore folder from the repository .zip file into the IDESDataPreparation folder. This will contain the test keys that the program will use.
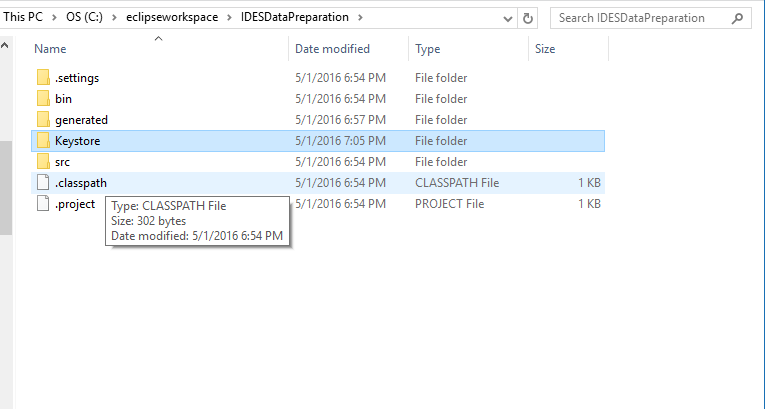
Figure 7
Certs
Place the Certs folder from the repository .zip file into the IDESDataPreparation folder. This will contain the test certificates in .crt format that the program will use.
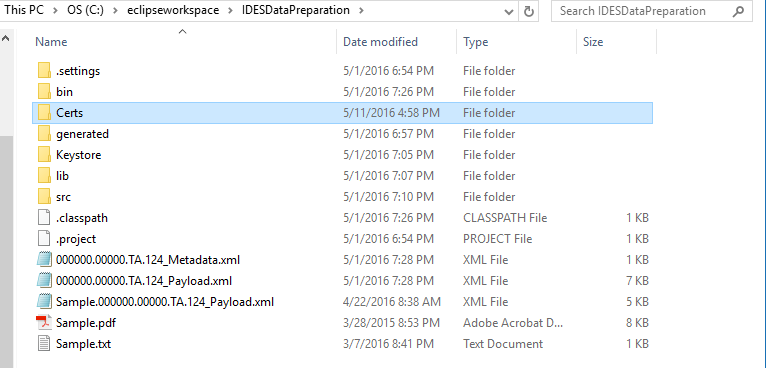
Figure 7-1
lib folder
Place the lib folder from the repository .zip file into the IDESDataPreparation folder. This will contain the .jar file for the console logging functionality.
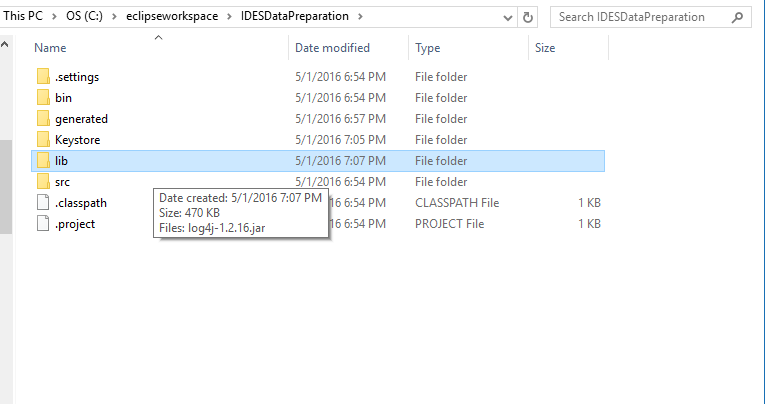
Figure 8
src folder
Add the src folder from the .zip repository into the IDESDataPreparation folder.
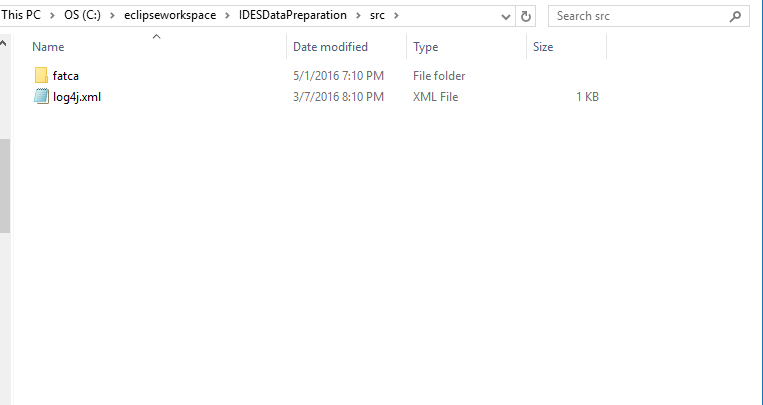
Figure 9
Test Payload file
Place the test Payload files from the repository .zip file into the root of the IDESDataPreparation folder. This is the FATCA Payload file that will be signed, encrypted, and packaged for transmission through IDES. Samples also exist for non-XML transfers.
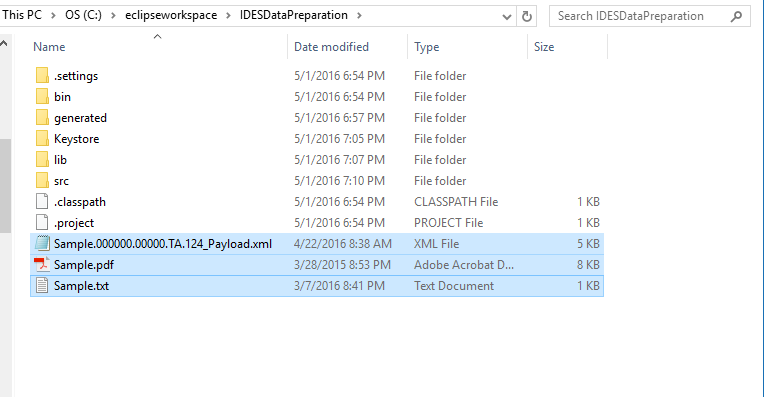
Figure 10
Test Configuration files
Place the sample Config files from the repository .zip file into the root of the IDESDataPreparation folder. These are sample configuration files that can be used to run the application with various settings.
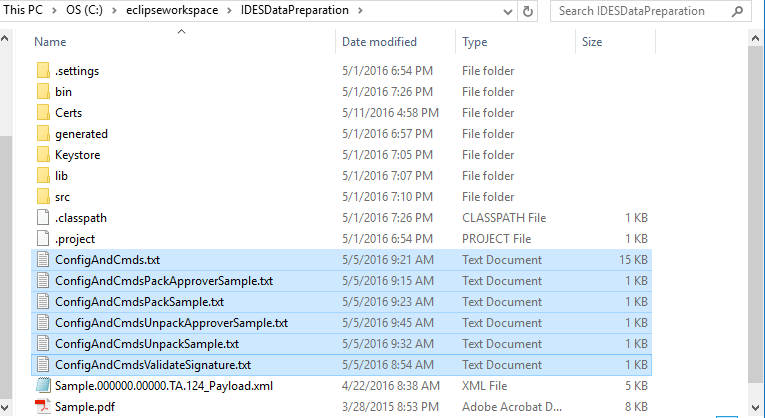
Figure 10-1
log4j.xml file
Place the log4j.xml file from the repository .zip file into the root of the IDESDataPreparation/bin folder. This is the settings file for the console logging .jar.
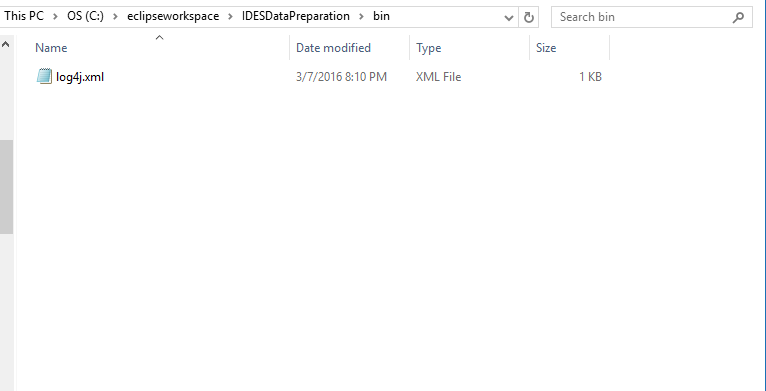
Figure 11
Project Contents
Refreshing the contents of the project will show the newly added folders and files:
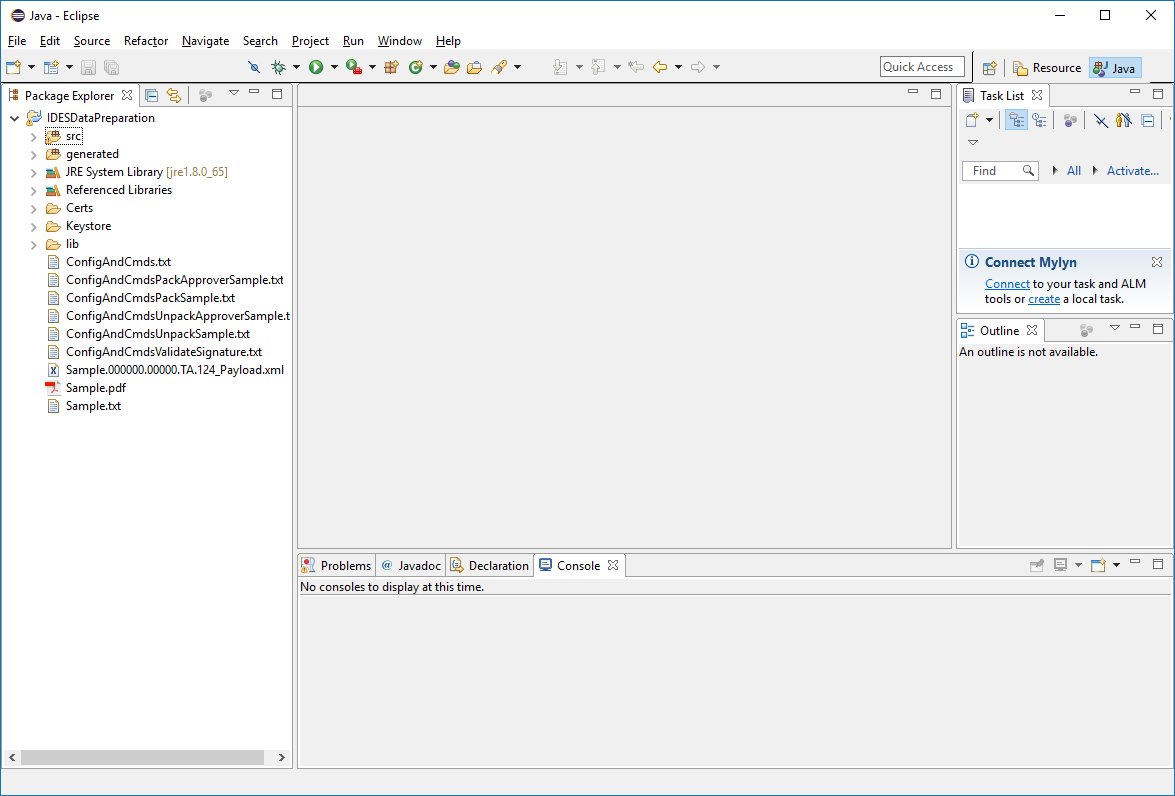
Figure 12
Project Properties
Enter the Project Properties screen and enter the Java Build Path selection:
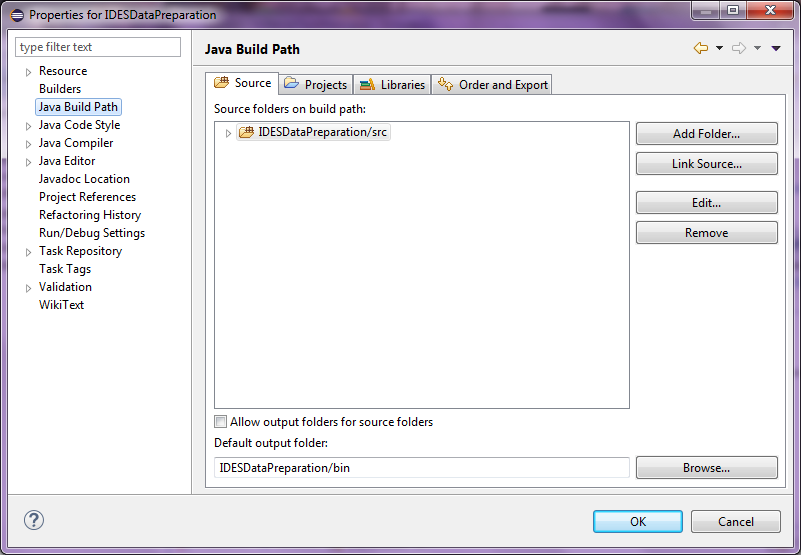
Figure 13
Add the generated folder to the Source tab and click OK
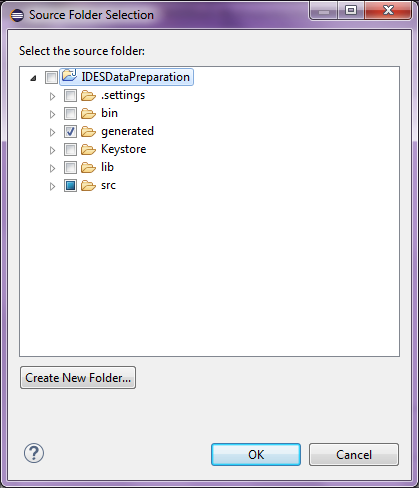
Figure 14
Updated Source tab
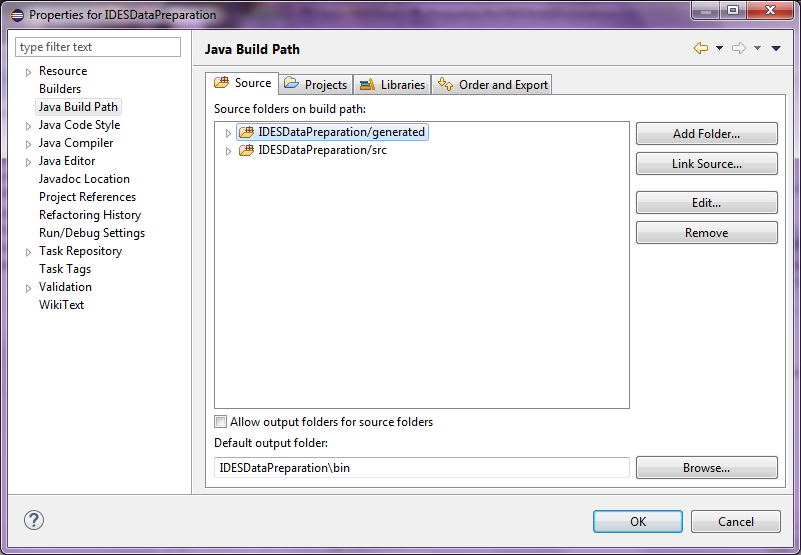
Figure 15
Select the Libraries tab
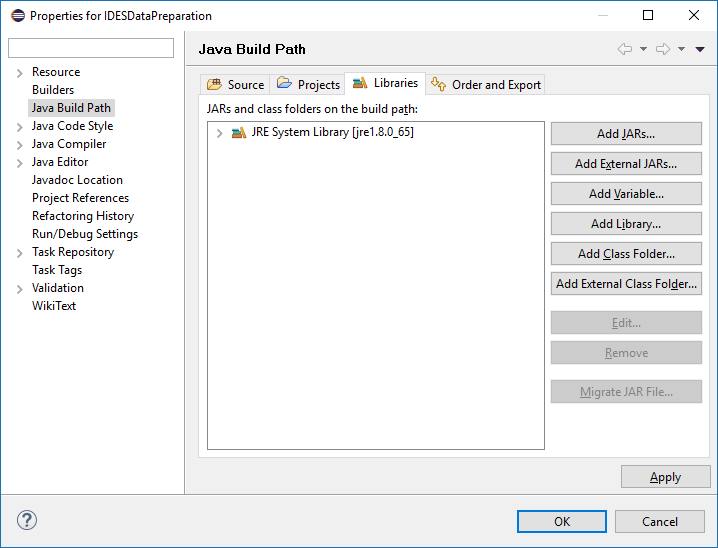
Figure 16
Select the Add JARs button and browse to the log4j-1.2.16.jar file in the lib folder and click the OK button to add:
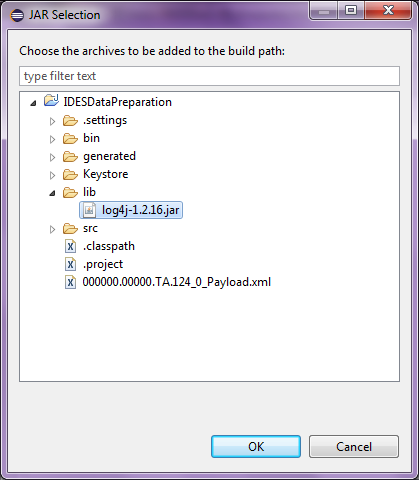
Figure 17
Updated Libraries tab
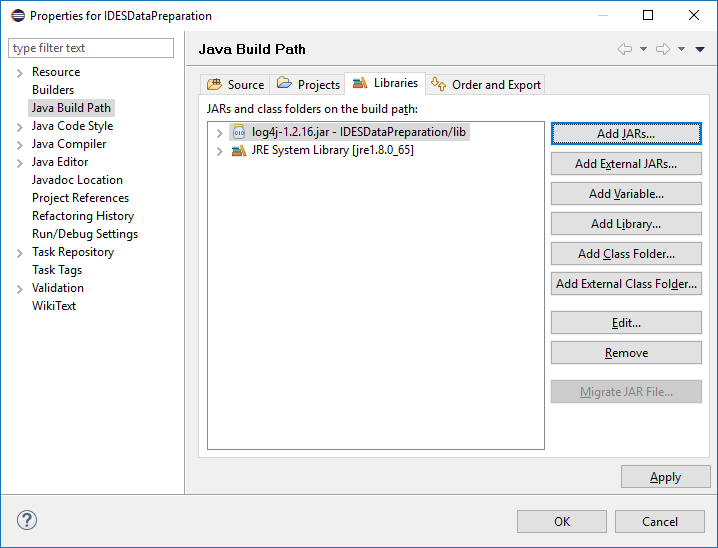
Figure 18
Run Configuration
Select the Run -> Run Configurations -> Java Application (from left panel) -> FATCADataPrepPETestTool (or the one created with another name) -> Arguments tab (from right panel tabs) -> VM Arguments (text box) and type -Dfile.encoding=UTF8 and click the Apply button.
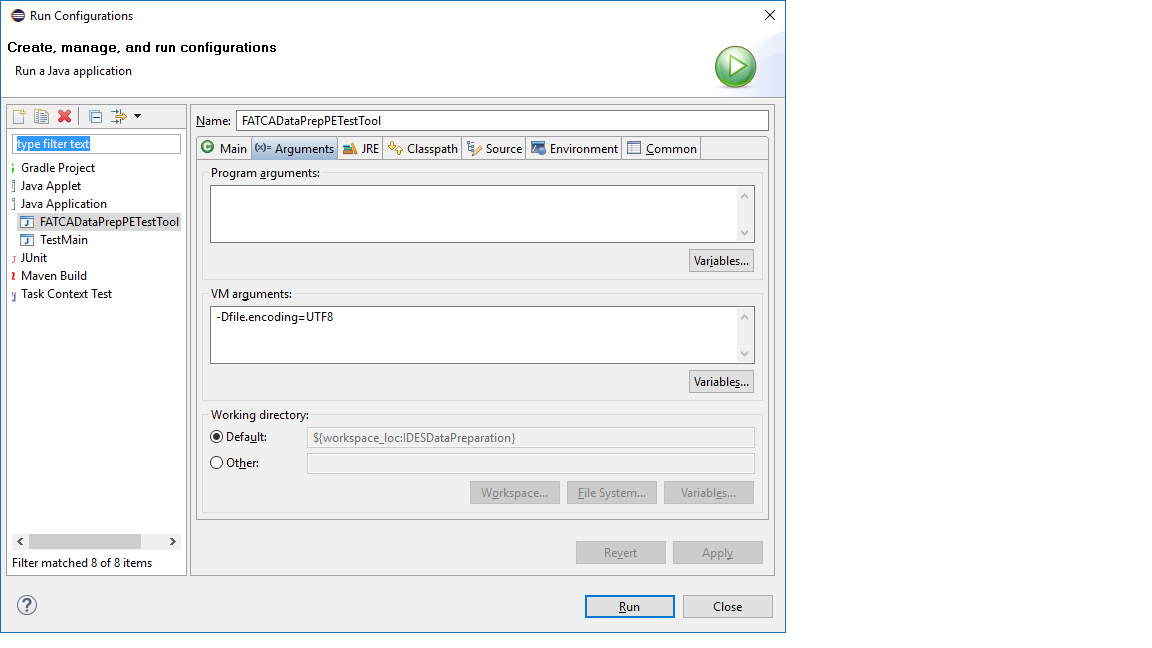
Figure 19
Running The Application
Open the FATCADataPrepPETestTool.java file located in the src\fatca\ folder and start the application. The Console tab will display the logging information from the program. This file will use the ConfigAndCmdsPackSample.txt file by default and has various settings for keys, model types, and non-XML testing as well as unpackaging notifications. This Config file can be replaced or modified as needed to test different scenarios. There are additional example Config files included in the repository.
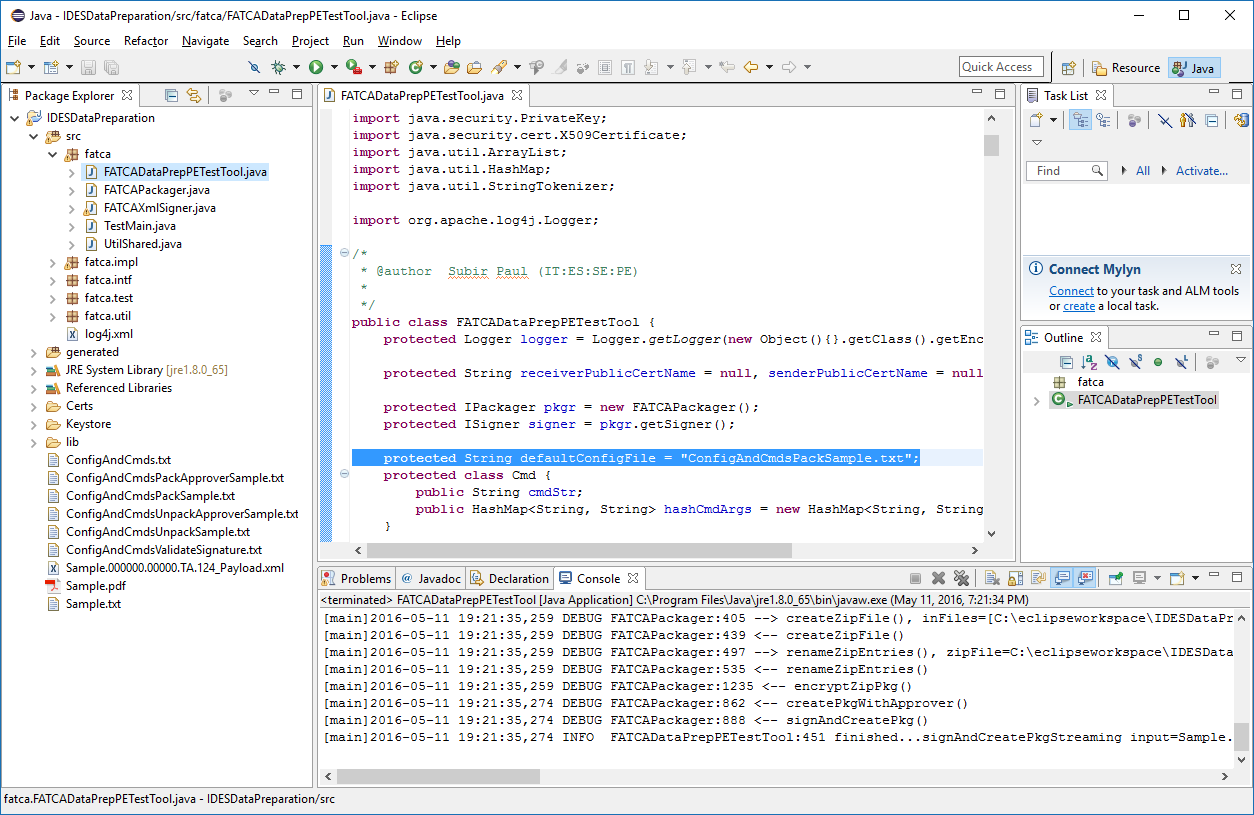
Figure 20
The output files will be placed in the root of the IDESDataPreparation folder:
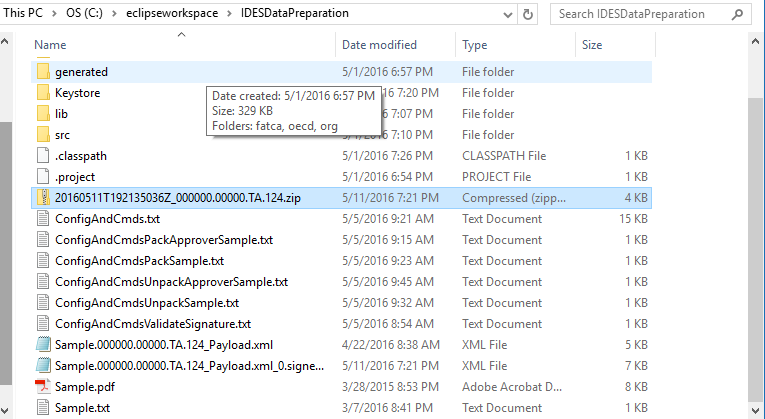
Figure 21
Disclaimer:
We waive copyright and related rights in the work worldwide through the CC0 1.0 Universal public domain dedication. Unless expressly stated otherwise, the person who associated a work with this deed makes no warranties about the work, and disclaims liability for all uses of the work, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law. When using or citing the work, you should not imply endorsement by the author or the affirmer.